Data Structure - Linked List (Concept and C++ code)
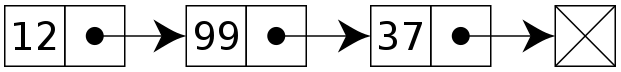
Linked List (단순연결리스트의 구조)
동적으로 크기가 변할 수 있고 삭제나 삽입 시에 데이터를 이동할 필요가 없는 구조
- 배열의 단점을 해결하는 자료구조
- 배열은 연결된 저장공간으로 미리 크기가고정된 데이터 구조
- 이에 반해서 Linked List 는 미리 크기를 고정하지 않고 필요할때마다 동적으로 추가,삭제가 가능한 데이터구조
- 노드(node) : 데이터 저장단위 (데이터, 포인터로 구성)
- 포인터(pointer) : 노드 안에서 노드의 다음 데이터에 대한 연결 정보(주소값)를 가지고 있는 공간
- Linked List 의 마지막 노드의 포인터는 nullptr로 설정
- 더이상 연결된 노드가 없다는 것을 의미
Linked List 의 장단점
- 장점
- 미리 데이터 공간을 할당하지 않아도 됨
- 단점
- 저장 효율이 높지 않음 (데이터 뿐만아니라 연결을 위한 포인터 주소공간도 필요하므로)
- 연결정보를 찾는 시간이 필요하므로 접근 속도가 느림
- 중간 데이터 삭제시, 앞뒤 데이터의 연결을 재구성해야함
C++ Code
- Linked List C++ code
- Below C++ code is for Singly Linked List
Node 구현 & Linked List class 구현
Linked List 에 데이터 추가하기
Linked List 데이터 출력하기
Node 와 Node를 연결하기
Linked List 데이터 사이에 데이터 추가하기
데이터 삭제하기
데이터 검색하기
node linkedlist 클래스
- Struct를 이용하여 Node만들기
#incldue <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node *next;
}
- Class를 이용하여 linked_list 만들기
- singly linked list에서 first node는 반드시 알고 있어야합니다.
- first node를 통해서 전체 list에 접근하므로
- first node를 head라고 함
- singly linked list에서 first node는 반드시 알고 있어야합니다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node *next;
}; //expected ';' after struct definition
class LinkedList
{
private:
node *head, *tail;
public:
LinkedList()
{
head = nullptr;
tail = nullptr;
}
}; //expected ';' after class definition
int main()
{
LinkedList l;
return 0;
}
데이터추가
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
node *head, *tail;
public:
LinkedList()
{
head = nullptr;
tail = nullptr;
}
void add_node(int n)
{
node *temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(head == nullptr) //no linked list yet, so current node will be the 'head' and 'tail' both. (as it is the last element right now)
{
head = temp;
tail = temp;
}
else //already have a linked list and we have to add the node at the end of the linked list.
{
tail->next = temp;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
};
int main()
{
LinkedList l;
l.add_node(10);
l.add_node(20);
return 0;
}
node *temp = new node; 새로운 node 객체 생성
temp->data = n; temp 노드의 data에 n값 입력
temp->next = nullptr; temp노드가 마지막 노드
tail->next = temp; 새로운 temp node가 tail 노드 다음에 위치
tail = tail->next; 새로운 노드는 새로운 tail노드
데이터출력
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node* next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
node *head, *tail;
public:
LinkedList()
{
head = nullptr;
tail = nullptr;
}
void add_node(int n)
{
node *temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(head == nullptr)
{
head = temp;
tail = temp;
}
else
{
tail->next = temp;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
void distplay()
{
node *temp;
temp = head; //temp = this->head;
while(temp != nullptr)
{
cout << temp->data << endl;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
};
int main()
{
LinkedList l;
l.add_node(10);
l.add_node(20);
l.distplay();
return 0;
}
temp = head;
- temp = this->head;
- 현재 객체의 head node
node연결
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node* next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
node *head, *tail;
public:
LinkedList()
{
head = nullptr;
tail = nullptr;
}
void add_node(int n)
{
node *temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(head == nullptr)
{
head = temp;
tail = temp;
}
else
{
tail->next = temp;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
node *gethead()
{
return head;
}
void distplay()
{
node *temp = head;
while(temp != nullptr)
{
cout <<temp->data <<endl;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
static void concatenate(node* a, node* b)
{
if( a!= nullptr && b != nullptr)
{
if(a->next == nullptr)
{
a->next = b;
}
else
{
concatenate(a->next, b);
}
}
else
{
cout << "Both nodes does not have data" <<endl;
}
}
};
int main()
{
LinkedList la;
la.add_node(10);
la.add_node(20);
la.distplay();
LinkedList lb;
lb.add_node(30);
lb.add_node(40);
lb.distplay();
LinkedList::concatenate(la.gethead(),lb.gethead());
la.distplay();
return 0;
}
데이터삽입
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node* next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
node* head;
node* tail;
public:
LinkedList()
{
head = nullptr;
tail = nullptr;
}
void add_node(int n)
{
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(head == nullptr)
{
head = temp;
tail = temp;
}
else
{
tail->next = temp;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
node* gethead()
{
return head;
}
void display(node * head)
{
if(head == nullptr)
{
cout << "nullptr : No data" << endl;
return;
}
else
{
node* temp;
temp = head;
while(temp != nullptr)
{
cout << temp->data << endl;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
void concatenate(node* a, node* b)
{
if(a!=nullptr && b!=nullptr)
{
if(a == nullptr)
{
a->next = b;
}
else
{
concatenate(a->next, b);
}
}
else
{
cout << "Both nodes does not have data" << endl;
}
}
void front(int n)
{
if(head == nullptr)
{
cout << "No data to insert in Linked list, call add_node function" <<endl;
return;
}
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = head;
head = temp; //***
}
void after(node* a, int value)
{
node*temp = new node;
temp->data = value;
temp->next = a->next;
a->next = temp; //***
}
};
int main()
{
LinkedList la;
la.add_node(10);
la.add_node(20);
la.add_node(30);
la.add_node(40);
la.add_node(50);
la.display(la.gethead()); //10 20 30 40 50
la.front(5);
la.after(la.gethead()->next->next, 25);
la.display(la.gethead()); //5 10 20 25 30 40 50
return 0;
}
데이터삭제
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node* next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
node* head;
node* tail;
public:
LinkedList()
{
head = nullptr;
tail = nullptr;
}
void add_node(int n)
{
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(head == nullptr)
{
head = temp;
tail = temp;
}
else
{
tail->next = temp;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
node* gethead()
{
return head;
}
void display(node * head)
{
if(head == nullptr)
{
cout << "nullptr : No data" << endl;
return;
}
else
{
node* temp;
temp = head;
while(temp != nullptr)
{
cout << temp->data << endl;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
void concatenate(node* a, node* b)
{
if(a!=nullptr && b!=nullptr)
{
if(a == nullptr)
{
a->next = b;
}
else
{
concatenate(a->next, b);
}
}
else
{
cout << "Both nodes does not have data" << endl;
}
}
void front(int n)
{
if(head == nullptr)
{
cout << "No data to insert in Linked list, call add_node function" <<endl;
return;
}
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = head;
head = temp;
}
void after(node* a, int value)
{
node*temp = new node;
temp->data = value;
temp->next = a->next;
a->next = temp;
}
void del(node* head, int value)
{
if(!head)
{
return;
}
else
{
node** nd = &head;
while(*nd && (*nd)->data != value)
nd = &(*nd)->next;
if(*nd)
{
node* temp = *nd;
*nd = (*nd)->next;
delete temp;
}
else
{
cout << "No matching data in the node" <<endl;
}
}
}
};
int main()
{
LinkedList la;
la.add_node(10);
la.add_node(20);
la.add_node(30);
la.add_node(40);
la.add_node(50);
la.display(la.gethead()); //10 20 30 40 50
la.front(5);
la.after(la.gethead()->next->next, 25);
la.display(la.gethead()); //5 10 20 25 30 40 50
la.del(la.gethead(), 40);
la.display(la.gethead()); //5 10 20 25 30 50
return 0;
}
데이터검색
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node* next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
node* head;
node* tail;
public:
LinkedList()
{
head = nullptr;
tail = nullptr;
}
void add_node(int n)
{
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(head == nullptr)
{
head = temp;
tail = temp;
}
else
{
tail->next = temp;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
node* gethead()
{
return head;
}
void display(node * head)
{
if(head == nullptr)
{
cout << "nullptr : No data" << endl;
return;
}
else
{
node* temp;
temp = head;
while(temp != nullptr)
{
cout << temp->data << endl;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
void concatenate(node* a, node* b)
{
if(a!=nullptr && b!=nullptr)
{
if(a == nullptr)
{
a->next = b;
}
else
{
concatenate(a->next, b);
}
}
else
{
cout << "Both nodes does not have data" << endl;
}
}
void front(int n)
{
if(head == nullptr)
{
cout << "No data to insert in Linked list, call add_node function" <<endl;
return;
}
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = n;
temp->next = head;
head = temp;
}
void after(node* a, int value)
{
node*temp = new node;
temp->data = value;
temp->next = a->next;
a->next = temp;
}
void del(node* head, int value)
{
if(!head)
{
return;
}
else
{
node** nd = &head;
while(*nd && (*nd)->data != value)
nd = &(*nd)->next;
if(*nd)
{
node* temp = *nd;
*nd = (*nd)->next;
delete temp;
}
else
{
cout << "No matching data in the node" <<endl;
}
}
}
bool search(node* a, int n)
{
if( a == nullptr)
{
cout << "node is empty" << endl;
return false;
}
else
{
node* temp = a;
while( temp != nullptr)
{
if( temp->data == n )
return true;
temp = temp->next;
}
return false;
}
}
};
int main()
{
LinkedList la;
la.add_node(10);
la.add_node(20);
la.add_node(30);
la.add_node(40);
la.add_node(50);
la.display(la.gethead()); //10 20 30 40 50
la.front(5);
la.after(la.gethead()->next->next, 25);
la.display(la.gethead()); //5 10 20 25 30 40 50
la.del(la.gethead(), 40);
la.display(la.gethead()); //5 10 20 25 30 50
la.search(la.gethead(), 30) ? (cout << "YES" << endl) : (cout << "NO" <<endl) ; //YES
return 0;
}
Singly Linked List - C++ Container library
c++ forward_list(singly linked list).
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Create a list containing integers
forward_list<int> fl = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
// Iterate and print values of the list
for (int n : fl) {
cout << n << '\n'; //1, 2, 3, 4
}
fl.pop_front();
for (int n : fl) {
cout << n << '\n'; //2, 3, 4
}
fl.push_front(5);
for (int n : fl) {
cout << n << '\n'; //5, 2, 3, 4
}
}
Doubly Linked List 이중 연결 리스트
- 더블 링크드 리스트 (Doubly Linked list) 구조
- singly linked list는 데이터 탐색시 head 노드부터 tail까지 탐색을 해야함 -> 원하는 데이터가 뒤에 있다면?
- 노드 탐색이 양쪽으로 가능한 Double Linked list
- 더블 링크드 리스트의 Node의 구조는 이전데이터주소 , 데이터, 다음 데이터 주소 로 이루어져있음
- singly linked list는 데이터 탐색시 head 노드부터 tail까지 탐색을 해야함 -> 원하는 데이터가 뒤에 있다면?
stl
Doubly Linked List - C++ Container library
c++ list (doubly linked list).
- list
lt(10) - lt 연결리스트에 10개의 요소를 default 0 값으로 생성 및 초기화
- list
lt{10} - lt 연결리스트에 10이라는 데이터를 하나 생성
- list
words1 {"I", "love", "Sunny", "weather"}; - workds 리스트 초기화
- list
words2(words1.begin(), words1.end()); - words2 == words1 연결 리스트 복사
- list
words3(words1); - words3 == words1 연결 리스트 복사
- list
words4(5, "Sunny"); - words4 {“Sunny”,”Sunny”,”Sunny”,”Sunny”,”Sunny”}
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Create a list containing integers
list<int> l = { 7, 5, 16, 8 };
// Add an integer to the front of the list
l.push_front(25);
// Add an integer to the back of the list
l.push_back(13);
// Insert an integer before 16 by searching
auto it = find(l.begin(), l.end(), 16);
if (it != l.end()) {
l.insert(it, 42);
}
// Iterate and print values of the list
for (int n : l) {
cout << n << '\n'; //25, 7, 5, 42, 16, 8, 13
}
l.pop_front();
for (int n : l) {
cout << n << '\n'; //7, 5, 42, 16, 8, 13
}
l.pop_back();
for (int n : l) {
cout << n << '\n'; //7, 5, 42, 16, 8
}
}