AWS - AWS Cloud Technical Essentials_week2
Work hard, have fun, and make history.
AWS Cloud Technical Essentials
AWS Cloud Technical Essentials - Week2
Compute as a Service on AWS
- Introduction to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
- In AWS, these virtual machines are called Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud or Amazon EC2. Behind the scenes, AWS operates and manages the host machines and the hypervisor layer. AWS also installs the virtual machine operating system, called the guest operating system.
- What Is Amazon EC2?
- virtual servers
- You can create and manage these instances through the AWS Management Console, the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI), AWS Software Development Kits (SDKs), or through automation tools and infrastructure orchestration services.
-
In order to create an EC2 instance, you need to define:
- Hardware specifications, like CPU, memory, network, and storage.
- Logical configurations, like networking location, firewall rules, authentication, and the operating system of your choice.
- What Is an AMI?
- In the traditional infrastructure world, the process of spinning up a server consists of installing an operating system from installation disks, installation drives, or installation wizards over the network. In the AWS Cloud, this operating system installation is no longer your responsibility, and is instead built into the AMI that you choose.
- What Is the Relationship Between AMIs and EC2 Instances?
- EC2 instances are live instantiations of what is defined in an AMI
Amazon EC2 Instance Lifecycle
- What Makes Up an EC2 Instance?
- EC2 instances are a combination of virtual processors (vCPUs), memory, network, and in some cases, instance storage and graphics processing units (GPUs).
- Where Does Your EC2 Instance Live?
- By default, your EC2 instances are placed in a network called the default Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). This network was created so that you can easily get started with Amazon EC2 without having to learn how to create and configure a VPC.
- Explore the EC2 Instance Lifecycle
- When you launch an instance, it enters the pending state (1)
- When your instance is running (2), it’s ready to use.
- When you reboot an instance (3), it’s different than performing a stop action and then a start action. Rebooting an instance is equivalent to rebooting an operating system. The instance remains on the same host computer and maintains its public and private IP address, and any data on its instance store.
- When you stop and start an instance (4), your instance may be placed on a new underlying physical server. Therefore, you lose any data on the instance store that were on the previous host computer. When you stop an instance, the instance gets a new public IP address but maintains the same private IP address.
- When you terminate an instance (5), the instance store are erased, and you lose both the public IP address and private IP address of the machine. Termination of an instance means you can no longer access the machine.
- Exercise 3: Launch the Employee Directory Application on Amazon EC2
Container Services on AWS
- What Is a Container?
- A container is a standardized unit that packages up your code and all of its dependencies. This package is designed to run reliably on any platform, because the container creates its own independent environment. This makes it easy to carry workloads from one place to another, such as from development to production or from on-premises to the cloud.
- What Is Docker?
- Docker is a popular container runtime that simplifies the management of the entire operating system stack needed for container isolation, including networking and storage. Docker makes it easy to create, package, deploy, and run containers.
- What Is the Difference Between Containers and VMs?
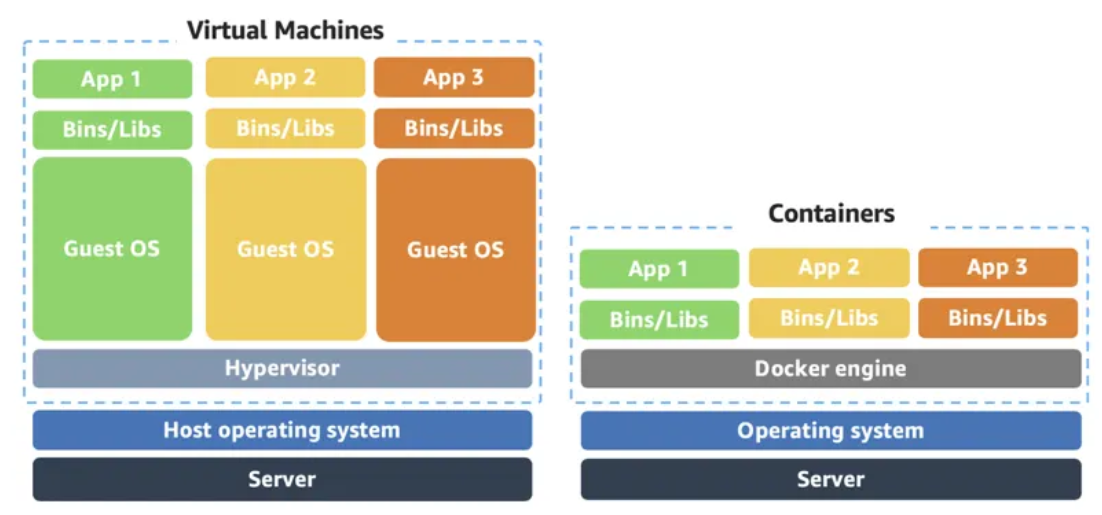
- Containers share the same operating system and kernel as the host they exist on, whereas virtual machines contain their operating system. Since each virtual machine has to maintain a copy of an operating system, there’s a degree of wasted space.
- A container is more lightweight. They spin up quicker, almost instantly. This difference in startup time becomes instrumental when designing applications that need to scale quickly during input/output (I/O) bursts.
- While containers can provide speed, virtual machines offer you the full strength of an operating system and offer more resources, like package installation, a dedicated kernel, and more.
- Orchestrate Containers
- In AWS, containers run on EC2 instances.
- If you’re trying to manage your compute at a large scale, coordination is needed
- coordination is handled by a container orchestration service.
- AWS offers two container orchestration services: Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
- Use Kubernetes with Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS)
-
Kubernetes is a portable, extensible, open source platform for managing containerized workloads and services. By bringing software development and operations together by design, Kubernetes created a rapidly growing ecosystem that is very popular and well established in the market.
-
Amazon EKS is conceptually similar to Amazon ECS, but there are some differences.
- An EC2 instance with the ECS Agent installed and configured is called a container instance. In Amazon EKS, it is called a worker node.
- An ECS Container is called a task. In the Amazon EKS ecosystem, it is called a pod.
- While Amazon ECS runs on AWS native technology, Amazon EKS runs on top of Kubernetes.
- If you have containers running on Kubernetes and want an advanced orchestration solution that can provide simplicity, high availability, and fine-grained control over your infrastructure, Amazon EKS is the tool for you.
-
What is Serverless?
Serverless means that you can not see or access the underlying infrastructure or instances that are hosting your solution.
- AWS Fargate.
- One example of serverless compute is AWS Fargate.
- AWS Fargate is a serverless compute platform that you can run either ECS or EKS on top of.
- Previously, you learned that ECS and EKS run on clusters of EC2 instances. And in that case, you are using EC2 as the compute platform for your containers, and you also have tight control over those instances.
- With AWS Fargate as the compute platform, you run your containers on a managed serverless compute platform. The scaling and fault-tolerance is built in and you don’t need to worry about the underlying operating system or the environment. Instead, you just define your container, how you want your container to be run and then it scales on-demand.
- 서버리스
- Serverless 가 말 그대로 server 가 없는 backend를 의미하는 것은 아니고
-
Serverless는 Backend without server MGMT(management)
- Serverless는 Backend를 서버에 올리는 것이아니라
- 서버리스에서는 백엔드를 작은 함수단으로 쪼개서 너가 직접관리하지 않는 서버로 올려.
- 예를들면, AWS lambda
- Serverless가 아닌 경우, 서버는 24시간 돌아가고있지.
- 언제나 요청에 응답할 준비를 하고있어
- Serverless의 경우, 너가 업로드한 함수는 잠을 자고 있어. 그러나 리퀘스트가 오는 순간 AWS는 함수를 깨울 것이고 요청한 작업을 수행하고 다시 함수는 잠에 들거야.
- 바로 위와같은 점이 서버리스의 혁명~~
- 즉, 24시간 동안 깨어서 대기안해도 된다는 것
- 서버리스에서는 너가 수행한 함수만큼만 돈을 내면 됨
Introduction to AWS Lambda
-
AWS Lambda function handler
def handler_name(event, context):
...
return some_value
def lamda_handler(event, context):
print(event)
return event['left'] + event['right']
- trigger
- AWS 람다함수는 기존의 AWS 서비스들과 연동이 됩니다.
- ex) AWS S3 속성에 람다함수를 추가하면 S3에 새로운 파일이 업로드될 때마다 람다함수가 실행되도록 설정 가능
Networking on AWS
VPC : Amazon Virtual Private Cloud
- What Is Networking?
- Networking is how you connect computers around the world and allow them to communicate with one another. In this trail, you’ve already seen a few examples of networking. One is the AWS global infrastructure. AWS has created a network of resources using data centers, Availability Zones, and Regions.
- What Are IP Addresses?
- In order to properly route your messages to a location, you need an address.
- each computer has an IP address. The IP address uses a combination of bits, 0s and 1s.
- What Is IPv4 Notation?
- Typically, you don’t see an IP address in this binary format. Instead, it’s converted into decimal format and noted as an Ipv4 address.
- In the end, this is what is called an Ipv4 address. This is important to know when trying to communicate to a single computer. But remember, you’re working with a network. This is where CIDR Notation comes in.
- Use CIDR Notation
- Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
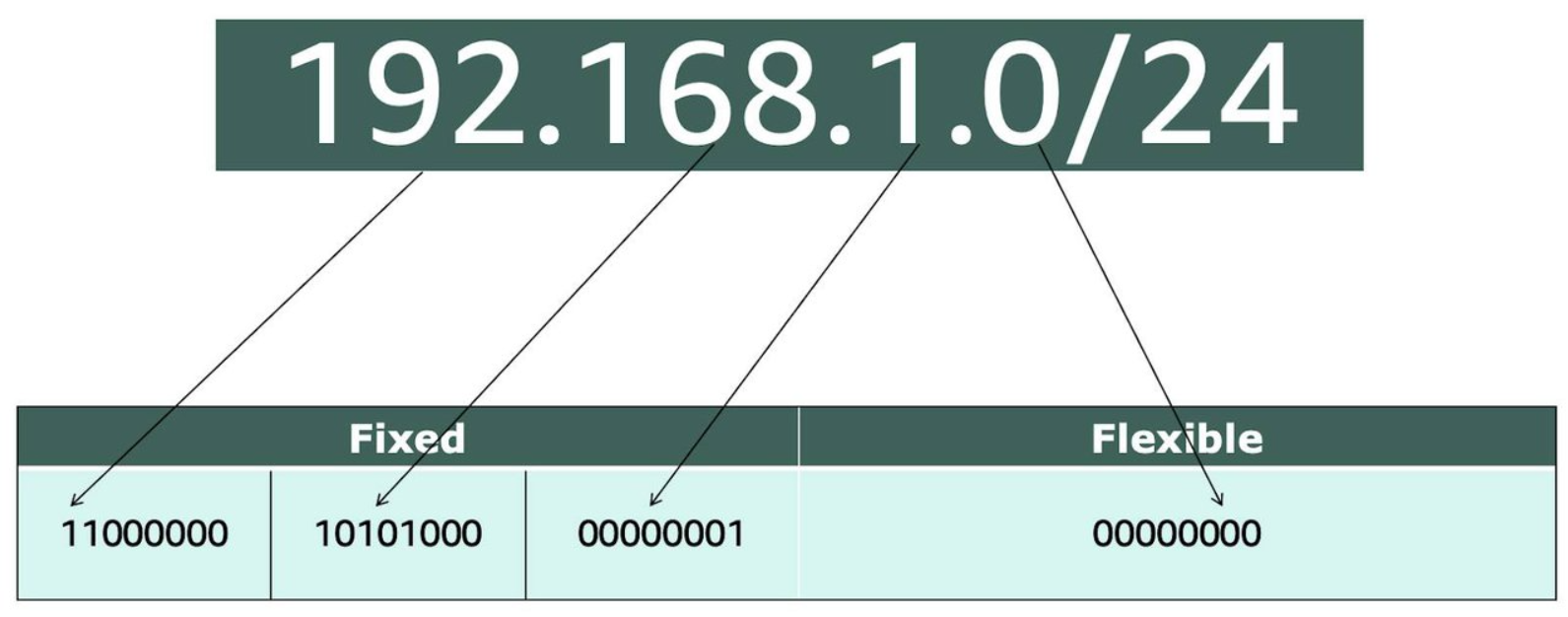
- 192.168.1.30 is a single IP address. If you wanted to express IP addresses between the range of 192.168.1.0 and 192.168.1.255, how can you do that?
- One way is by using CIDR notation. CIDR notation is a compressed way of specifying a range of IP addresses. Specifying a range determines how many IP addresses are available to you.
- It begins with a starting IP address and is separated by a forward slash (the “/” character) followed by a number. The number at the end specifies how many of the bits of the IP address are fixed. In this example, the first 24 bits of the IP address are fixed. The rest are flexible.
-
32 total bits subtracted by 24 fixed bits leaves 8 flexible bits. Each of these flexible bits can be either 0 or 1, because they are binary. That means you have two choices for each of the 8 bits, providing 256 IP addresses in that IP range.
-
The higher the number after the /, the smaller the number of IP addresses in your network. For example, a range of 192.168.1.0/24 is smaller than 192.168.1.0/16.
- When working with networks in the AWS Cloud, you choose your network size by using CIDR notation. In AWS, the smallest IP range you can have is /28, which provides you 16 IP addresses. The largest IP range you can have is a /16, which provides you with 65,536 IP addresses.
Introduction to Amazon VPC
- Create a VPC
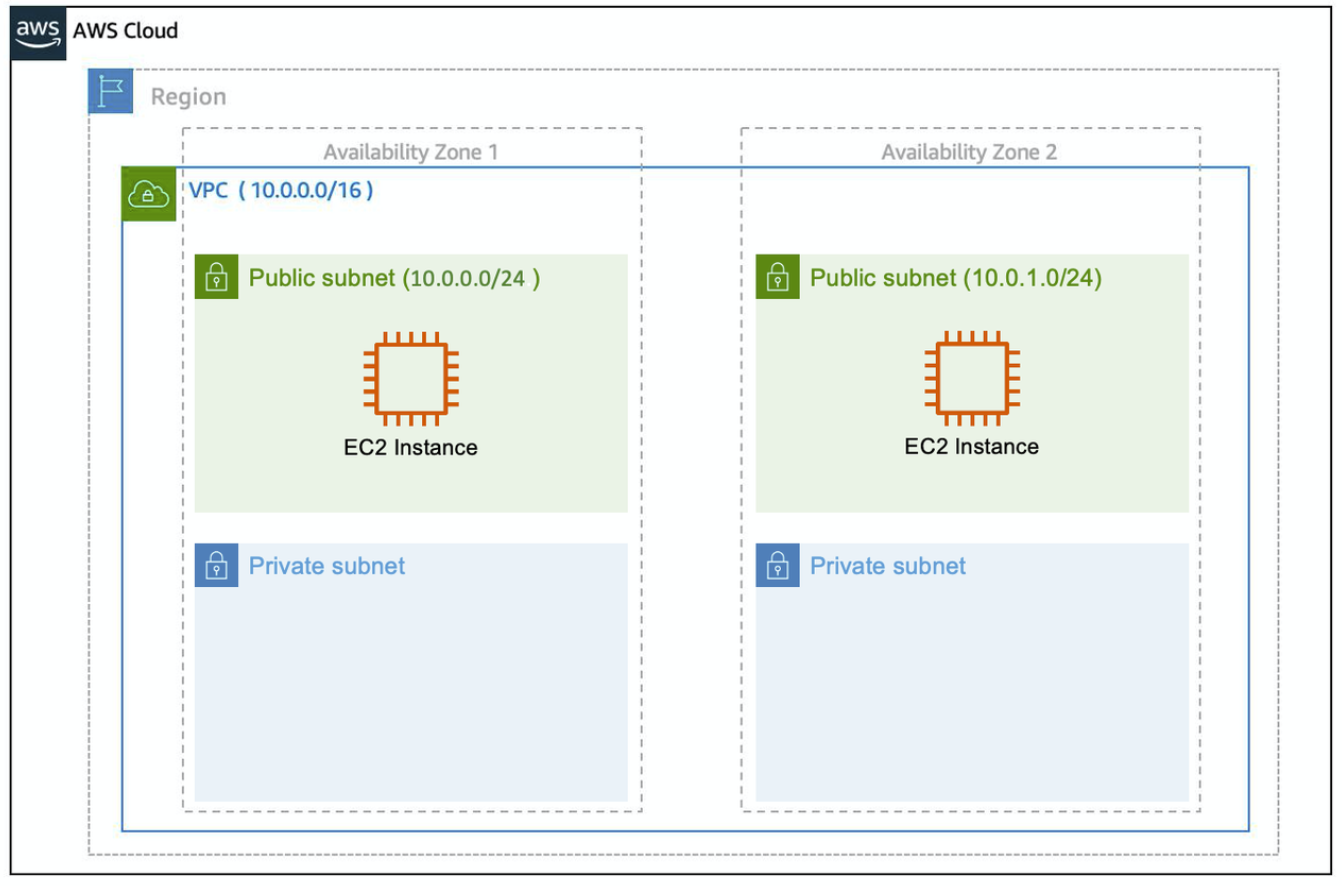
- A VPC is an isolated network you create in the AWS cloud, similar to a traditional network in a data center. When you create a VPC, you need to choose three main things.
- The name of your VPC.
- A Region for your VPC to live in. Each VPC spans multiple Availability Zones within the Region you choose.
- A IP range for your VPC in CIDR notation. This determines the size of your network. Each VPC can have up to four /16 IP ranges.
- A VPC is an isolated network you create in the AWS cloud, similar to a traditional network in a data center. When you create a VPC, you need to choose three main things.
- Create a Subnet
- After you create your VPC, you need to create subnets inside of this network.
- Think of subnets as smaller networks inside your base network—or virtual area networks (VLANs) in a traditional, on-premises network.
- In an on-premises network, the typical use case for subnets is to isolate or optimize network traffic. In AWS, subnets are used for high availability and providing different connectivity options for your resources.
- When you create a subnet, you need to choose three settings.
- The VPC you want your subnet to live in, in this case VPC (10.0.0.0/16).
- The Availability Zone you want your subnet to live in, in this case AZ1.
- A CIDR block for your subnet, which must be a subset of the VPC CIDR block, in this case 10.0.0.0/24.
Gateways
- Internet Gateway
- To enable internet connectivity for your VPC, you need to create an internet gateway. Think of this gateway as similar to a modem. Just as a modem connects your computer to the internet, the internet gateway connects your VPC to the internet. Unlike your modem at home, which sometimes goes down or offline, an internet gateway is highly available and scalable. After you create an internet gateway, you then need to attach it to your VPC.
- Virtual Private Gateway
- A virtual private gateway allows you to connect your AWS VPC to another private network.
- Once you create and attach a VGW to a VPC, the gateway acts as anchor on the AWS side of the connection. On the other side of the connection, you’ll need to connect a customer gateway to the other private network. A customer gateway device is a physical device or software application on your side of the connection. Once you have both gateways, you can then establish an encrypted VPN connection between the two sides.
Amazon VPC Routing
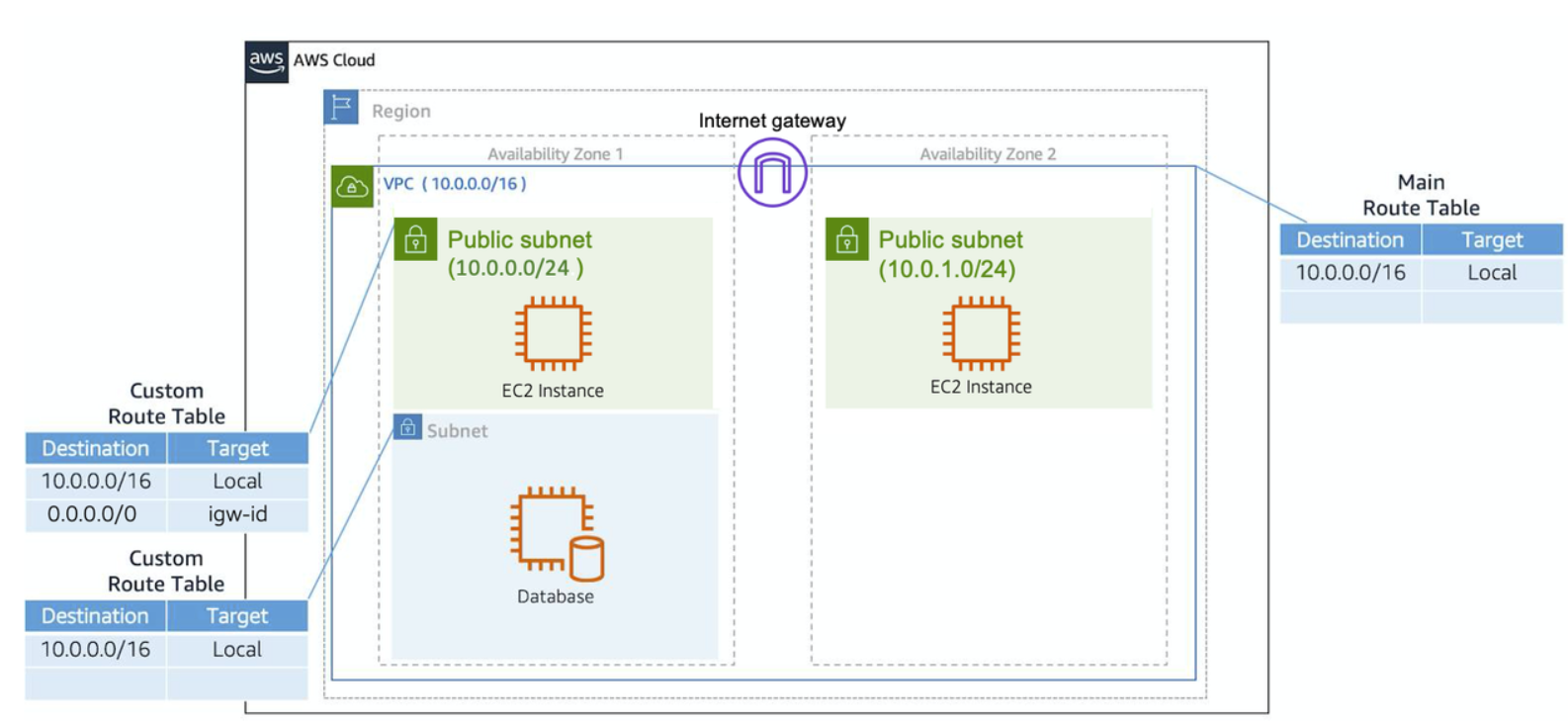
- The Main Route Table
- When you create a VPC, AWS creates a route table called the main route table. A route table contains a set of rules, called routes, that are used to determine where network traffic is directed. AWS assumes that when you create a new VPC with subnets, you want traffic to flow between them. Therefore, the default configuration of the main route table is to allow traffic between all subnets in the local network.
- Custom Route Tables
- While the main route table controls the routing for your VPC, you may want to be more granular about how you route your traffic for specific subnets.
- If you associate a custom route table with a subnet, the subnet will use it instead of the main route table. By default, each custom route table you create will have the local route already inside it, allowing communication to flow between all resources and subnets inside the VPC.
- Secure Your Subnets with Network ACLs(access control lists)
- A network ACL secures subnets
- Think of a network ACL as a firewall at the subnet level. A network ACL enables you to control what kind of traffic is allowed to enter or leave your subnet. You can configure this by setting up rules that define what you want to filter.
- Secure Your EC2 Instances with Security Groups
- a security group is responsible for securing EC2 instances.
- The next layer of security is for your EC2 Instances. Here, you can create a firewall called a security group.
Exercise 4: Creating a VPC and relaunching the Corporate Directory Application on Amazon EC2
Week 2 Assessment and Discussion(6/11)
Question 1 (X)
- Which of the following pieces of information do you need to create a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)?
- The Availability Zone it will reside in.
- The subnet it will reside in.
- The AWS Region it will reside in.
- The group of subnets it will reside in.
Question 2 (X)
- Which of the following can a route table be attached to?
- AWS Accounts
- Availability Zone
- Subnets
- Regions
Question 3 (X)
- What must you do to allow resources in a public subnet to communicate with the internet?
- A) Create a route to a private subnet.
- B) Attach an internet gateway to your VPC.
- C) Create a route in a route table to the internet gateway.
- A and B
- B and C
Question 4
- True or false: A network ACL filters traffic at the EC2 instance level.
- True
- False
Question 5
- Which of the following is true for the default settings of a security group?
- Allows all inbound traffic and blocks all outbound traffic.
- Blocks all inbound traffic and allows all outbound traffic.
- Allows all inbound and outbound traffic.
- Blocks all inbound and outbound traffic.
- What is inbound traffic?
- Inbound or Outbound is the direction traffic moves between networks. It is relative to whichever network you are referencing. Inbound traffic refers to information coming-in to a network.
- Inbound traffic originates from outside the network, while outbound traffic originates inside the network.
Question 6 (X)
- What does an Amazon EC2 instance type indicate?
- Instance family and instance size
- Instance placement and instance size
- Instance tenancy and instance billing
- Instance AMI and networking speed
Question 7
- True or false: EC2 instances reside at the Availability Zone level, so it’s best practice to architect for high availability.
- True
- False
Question 8
- What is the difference between AWS Fargate and Amazon ECS on EC2?
- With AWS Fargate, AWS manages and provisions the underlying infrastructure for hosting your containers.
- With Amazon ECS on EC2, AWS manages and provisions the underlying EC2 instance for your containers.
- With AWS Fargate, you have to manage cluster capacity and scaling.
- With Amazon ECS on EC2, you only have to upload your source code and ECS takes care of the rest.
Question 9
- Which of the following is true about serverless?
- You must provision and manage servers.
- You must manually scale serverless resources.
- You never pay for idle resources.
- You must manage availability and fault tolerance.
Question 10
- True or false: AWS Lambda is always the best solution when running applications on AWS.
- True
- False
Question 11 (X)
- True or false: Amazon EC2 is best suited for applications where you need more convenience and less control.
- True
- False